Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the core of virtually all electronic devices today, from smartphones to industrial controllers. Understanding the most important components of a PCB isn’t just helpful for engineers; it’s valuable for anyone interested in how electronics really work.
Before exploring individual parts, let’s clarify: a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a flat, structured platform that organizes and connects electronic components using conductive tracks and pads. Without PCBs, modern electronic devices would be bulky, unreliable, and difficult to manufacture.
In embedded systems – whether for IoT products, smart devices, or industrial machinery – PCBs offer both a physical structure and an electrical backbone. At EmbedPro Ltd., we focus on designing reliable PCBs tailored specifically for embedded system applications, emphasizing both performance and durability from concept to production.
Key PCB components for embedded system design
While PCBs vary in complexity, there are several components you’ll find in almost every professional embedded system. Each serves a unique and essential purpose.
Resistors: controlling current flow in PCB circuits
Resistors are the workhorses of PCB design. Their main job is to regulate the flow of electrical current, preventing overload that could damage sensitive components.

But that’s not all. Resistors also divide voltages, control signal levels, and set biasing for active components like transistors. Choosing the correct resistor value and type is crucial for maintaining circuit stability, which directly impacts the performance and reliability of embedded systems.
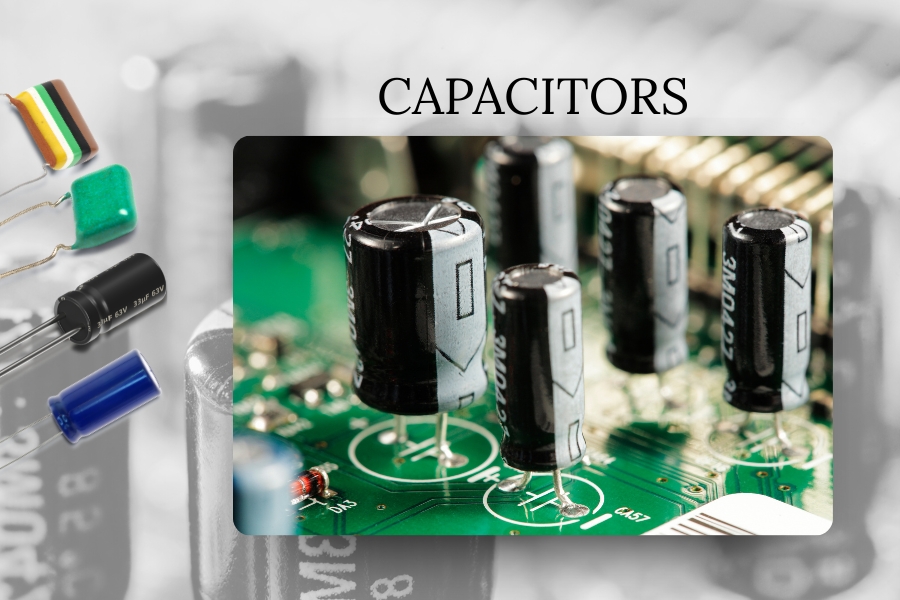
Capacitors: Storing and Releasing Energy Effectively
Capacitors store electrical energy temporarily and release it when needed. Their role becomes especially clear in power supply circuits where they smooth out voltage fluctuations.
In embedded systems, capacitors also filter signals, block direct current (DC) while allowing alternating current (AC) to pass, and provide energy storage in timing applications. Using the right type and size of capacitors improves system responsiveness and protects against voltage spikes.
Inductors: Managing Magnetic Fields in Complex PCB Designs
Inductors store energy in the form of magnetic fields. They may not appear in simple circuits, but in advanced PCB designs – such as those for industrial control systems – they’re indispensable.
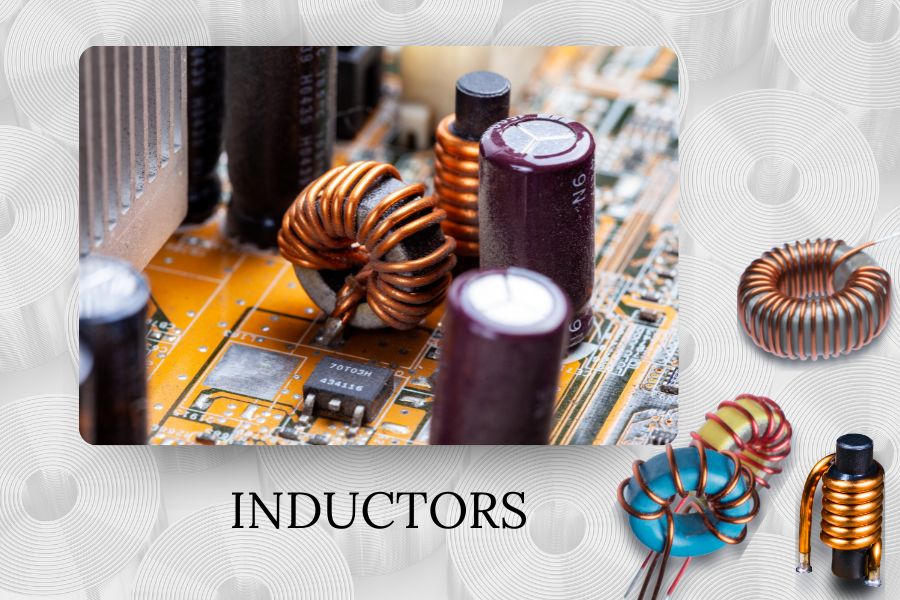
Inductors are common in power supply filtering, RF (radio frequency) circuits, and creating resonant circuits when combined with capacitors. These applications are critical in embedded systems that require high precision and stability.

Diodes: Ensuring Correct Current Direction in Embedded Systems
Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, serving as a protective gatekeeper for the circuit. In embedded systems, they are often used for reverse polarity protection – preventing damage when a power source is connected incorrectly.
They also play roles in voltage regulation, signal demodulation, and even light emission (as in LEDs). Proper placement of diodes ensures that embedded systems operate safely and predictably.
Transistors: Amplifying and Switching Signals in Embedded System PCBs
Transistors are perhaps the most transformative invention in electronics. These components act as electronic switches and amplifiers, controlling everything from signal flow to power distribution.
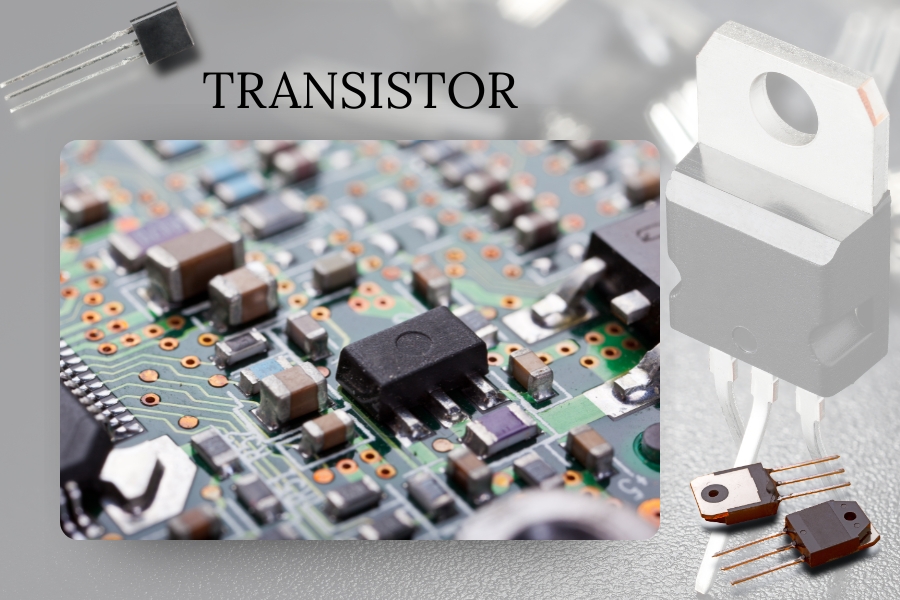
In embedded systems, transistors are used in logic gates, memory elements, and power regulation. Selecting the appropriate transistor type – bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), field-effect transistors (FETs), or others – directly influences energy efficiency, processing power, and device longevity.
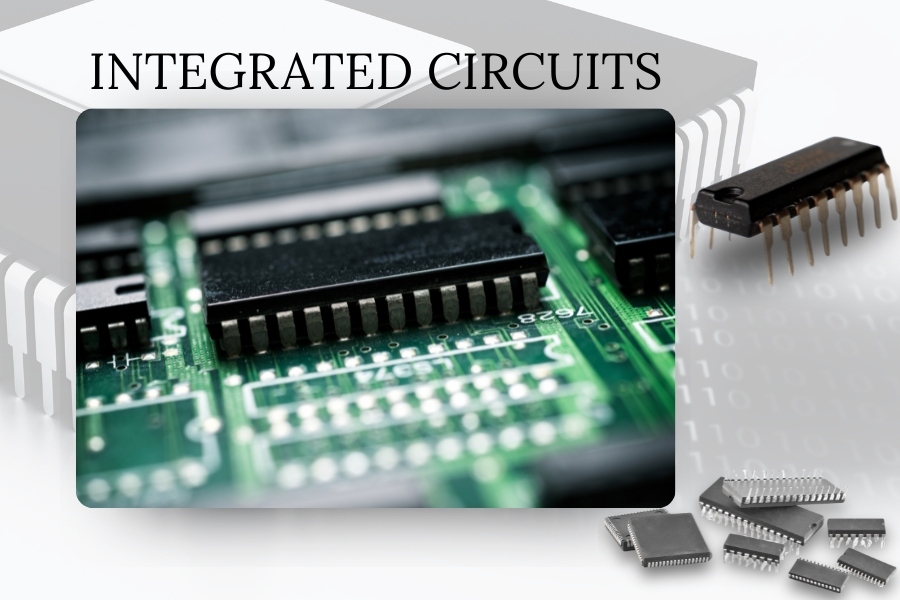
Integrated Circuits (ICs): Miniature Systems on a Chip for Embedded Devices
Integrated Circuits (ICs) are small chips that contain thousands, sometimes millions, of tiny components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors.
These miniaturized systems perform complex tasks like data processing, memory storage, and wireless communication. For embedded system design, ICs are non-negotiable. They allow for compact, efficient solutions that deliver powerful performance in a small footprint. Choosing the right IC involves balancing processing needs, power consumption, and space constraints.
Connectors: Linking PCB Assemblies to Devices and Power Sources
No PCB operates in isolation. Connectors provide the essential link between the PCB and the outside world – whether that’s a power supply, user interface, or sensor network.
In embedded systems, connectors can range from USB ports to specialized pin headers and industrial-grade terminals. High-quality connectors ensure reliability, especially in harsh environments like automotive or factory settings.
Why choosing the right PCB components matters for embedded system development
Every component on a PCB contributes to the system’s overall function, safety, and durability. In embedded systems, where size, power efficiency, and reliability are paramount, the choice of components isn’t just a technical detail – it’s a strategic decision.
Selecting poor-quality or mismatched components can lead to failures, wasted energy, and safety hazards. At EmbedPro Ltd., we prioritize choosing the right parts for each project, aligning our PCB designs with the specific demands of the product and its intended environment.
To summarize, understanding the most important components of a PCB – resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, and connectors – provides valuable insight into how modern electronics function.
Choosing these components wisely ensures performance, efficiency, and reliability. If you’re working on an embedded system that requires professional PCB design, we are here to help. Our team specializes in creating custom solutions built around your project’s unique requirements.

